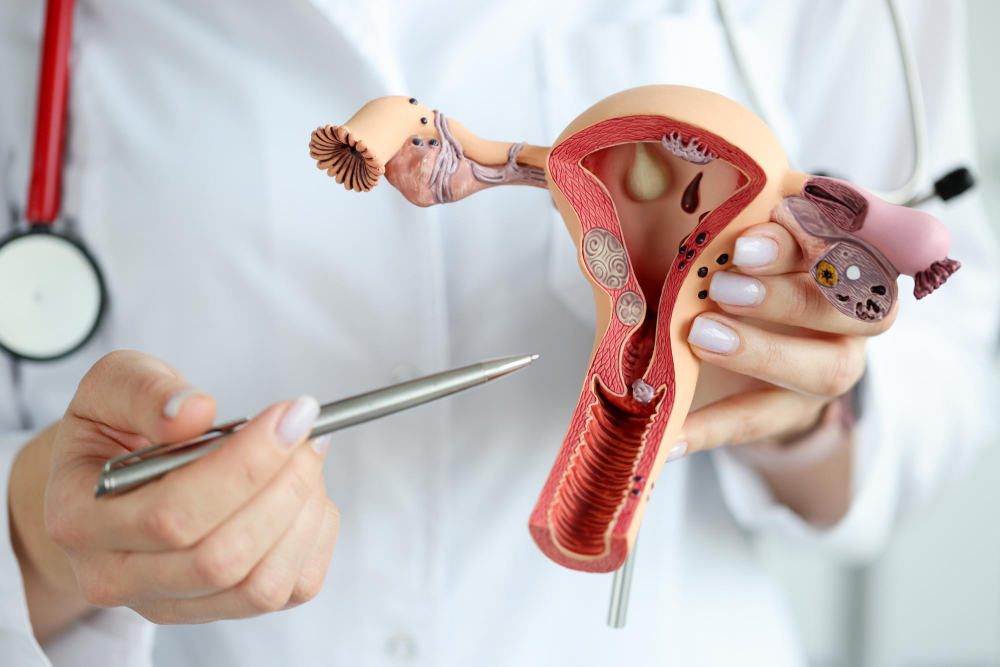
To most people, the word ‘pap smear’ does not sound familiar, and they may think it is a disease or a medical condition. A Pap smear, in fact, is not a disease; it is an effective diagnostic test that detects the presence of cancerous growth in the cervix of a woman. It is also called a pap test. The cervical region is the region that is present between your vagina and the uterus. Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer affecting women and is responsible for causing a higher number of deaths in developing countries. Cervical cancer is caused by a virus called the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which spreads through sexual contact. The immune system of your body is able to fight and defeat the HPV infection many times, but if you are at high risk for cervical cancer, the HPV infection may result in cancer. These abnormal cancerous cells are found by using a pap smear test. By getting a pap smear done regularly, you can find and treat these cells before they turn into cancer.
Preparing yourself for Pap smear
There are many things that can interfere with your test results; therefore, it is important that you follow a few dos and don’ts before going for a pap smear. It is suggested that 2 days before the test, you avoid:
- Douching (vaginal rinsing)
- Using tampons
- Using vaginal sprays or deodorants
- Using vaginal creams, suppositories, and medicines
- Having sex
- Taking a tub bath
- Using spermicidal foam
Pap smears are not done during periods. The best time to have a Pap smear done is between 10 and 20 days after your menstrual cycle.
Procedure
When you visit your doctor, he or she will ask you to lie down and place your feet in the stirrups to properly position your pelvis for examination. Now your doctor will put a special sterile instrument called a speculum into your vagina to open it so that she can take a sample from the cervix. Once the cervix is visible, she will wipe the cervix with a cotton swab and collect cells from the cervix using a small brush, spatula, or cotton swab. The collected sample will now be placed on a glass slide and sent to the laboratory for further investigation under a microscope.
The collected cervical cell sample is sent to the laboratory, where it is stained using a special dye (Pap stain) and viewed under a microscope. The cells are checked for signs of cancerous development. Before actually developing into a fully-fledged cancerous growth, the cervical cells undergo many stages. If the cells are caught before becoming cancerous and treated, cervical cancer is not life-threatening anymore. Therefore, it is very important that you have your pap smear done regularly.
Pap smear results
You will get your Pap smear result only after 3 weeks. The result will be given either as negative or positive.
Negative result: A negative result means that there were no cancerous or abnormal cells detected in your sample. You may not need any further tests.
Positive result: The following words will be used to describe results that were not normal:
- Benign changes: This means that your cells are normal but there is a high chance of developing an infection. Now your physician might do a detailed pelvic examination to find out the exact cause of the infection.
- Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS): This means that there are few abnormal cells present. This would require a few more tests to determine whether it is caused by HPV.
- Low-grade dysplasia (LSIL) and high-grade dysplasia (HSIL): This means that the cells are in a pre-cancerous condition.
- Carcinoma in situ: This means that abnormal cells are progressing into cancerous cells.
- Atypical squamous cells (ASC-H): This means abnormal cells are found and may be high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL).
If your Pap smear results are abnormal or show any abnormal cells, your doctor may recommend a few more tests to confirm or identify the cause of the abnormal result. Sometimes he may ask you to repeat your pap smear.
In the case of abnormal results, a few advanced tests that your doctor may perform are as follows:
- HPV test: This test detects the presence of cancer-causing HPV in the cervical cells.
- Colposcopy: It is a tool to examine vaginal or cervical cells in detail.
- Endocervical curettage: A small number of cells are scrapped from the endocervical region using a curette.
- Biopsy: A small sample of the cervical tissue is removed from the cervix and sent to the lab for further tests.
- LUMA cervical imaging system: A recently introduced advanced technique that is used right after colposcopy. This device examines the cervical cells that are suspected to have pre-cancerous cells. It further makes a colour map that helps your physician decide the area to perform a biopsy.
Pap smear for screening
It is usually recommended that you start having your Pap smear test done once you are sexually active or if you are over 18 years of age. You can also consult your doctor for a schedule of when to have a Pap smear done. You should have your Pap smear done repeatedly until you have 3 continuous normal results. After 3 normal results, you can talk to your doctor about spacing your Pap smear follow-up tests. It is recommended that you have your pap smear done at least once every 3 years, even after menopause, until your doctor says you no longer need it. If you are older than 65 years and have normal Pap results, then consult with your doctor before stopping the tests.
Pap smear reliability
As with any other test, pap smears may also show false positive or false negative results. This may be due to many factors, such as a small sample with too few cells to study. There may not be enough abnormal cells, or an infection or blood may mask the cells. In addition, vaginal rinsing or medication may wash away or dilute abnormal cells. In spite of this, the Pap smear is considered a very effective diagnostic tool if performed properly, as it has considerably reduced the number of deaths due to cervical cancer.
Ways to avoid cervical cancer
Following a few preventive measures helps to avoid cervical cancer.
- Do not indulge in sexual activity until you are 18 years old.
- Make sure that you and your partner get tested for sexually transmitted diseases.
- Have sex with a limited number of partners.
- Always have protected sex.
- Quit smoking.
Conclusion
Having an abnormal pap smear result is, of course, a reason to worry because abnormal cells may develop into cancerous cells in no time or increase the risk of cervical cancer. Talk to your doctor about the results and consult with him about what your results mean and what steps you should take next. Remember to do follow-up check-ups, as they help detect the problem at an earlier stage.